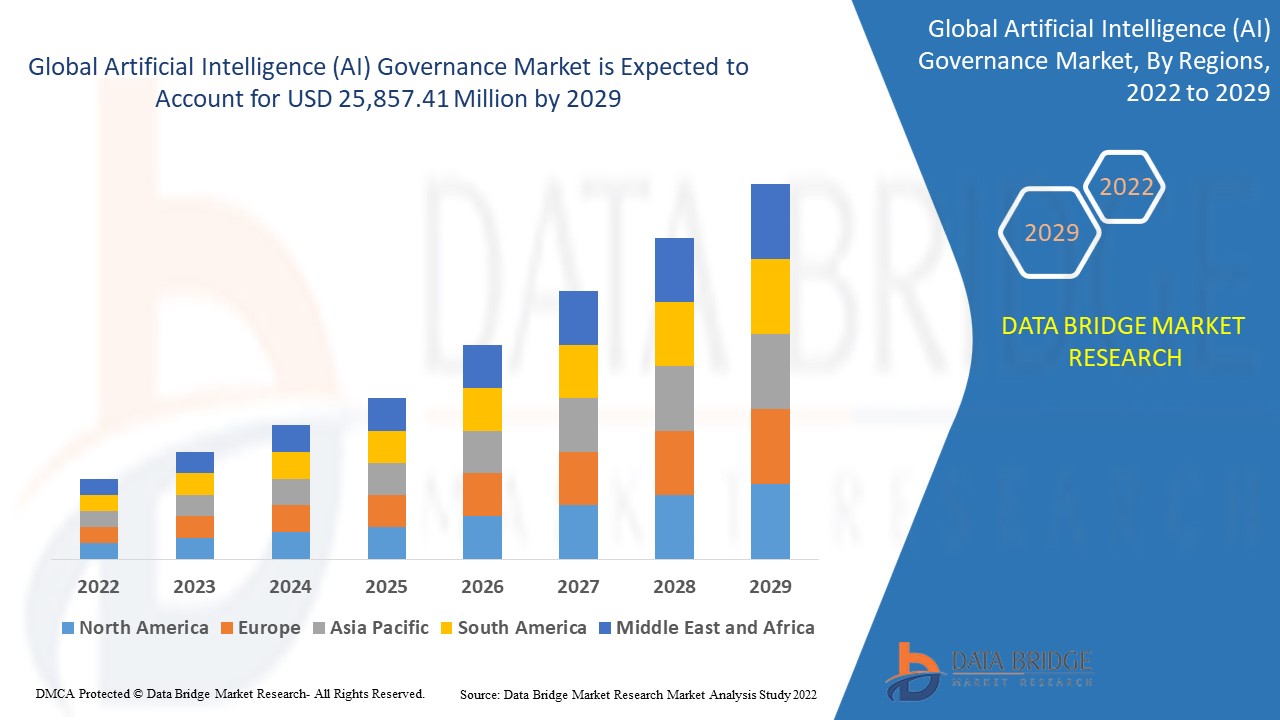
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to reshape industries and influence society, managing its ethical, legal, and operational implications has become a critical priority.Artificial Intelligence (AI) governance addresses these challenges by creating frameworks that guide the responsible development, deployment, and monitoring of AI systems.
In this guide, we explore the concept of AI governance, its importance, key principles, implementation strategies, challenges, and emerging trends shaping its future.
What is AI Governance?
AI governance refers to the policies, regulations, and frameworks that oversee the development and use of AI technologies. It aims to ensure that AI systems operate ethically, transparently, and responsibly, minimizing risks and maximizing societal benefits.
AI governance encompasses a wide range of practices, including:
- Establishing accountability for AI decision-making.
- Ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards.
- Managing risks related to bias, privacy, and misuse of AI.
- Promoting transparency and explainability in AI algorithms.
Why is AI Governance Important?
1. Mitigating Ethical Risks
AI systems can inadvertently reinforce biases, make unfair decisions, or lead to unintended consequences. Governance frameworks help mitigate these risks.
2. Ensuring Compliance
AI governance ensures adherence to data privacy laws, anti-discrimination regulations, and other legal standards, reducing liability risks.
3. Building Trust
Transparent and fair AI practices foster trust among stakeholders, including customers, employees, and regulators.
4. Encouraging Innovation
Governance provides a structured approach that allows organizations to innovate responsibly without compromising ethical standards.
5. Managing Operational Risks
By identifying and addressing potential failures, governance frameworks minimize disruptions caused by AI malfunctions or security breaches.
Core Principles of AI Governance
1. Transparency
AI systems should be designed and deployed in ways that are understandable to stakeholders, ensuring clear explanations of decision-making processes.
2. Accountability
Organizations must define accountability for AI outcomes, assigning responsibilities for monitoring and addressing system performance and impacts.
3. Fairness and Bias Mitigation
AI models should be developed to avoid discrimination and ensure equitable outcomes across different demographics.
4. Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security must be prioritized, ensuring that AI systems comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
5. Human Oversight
AI governance frameworks should include provisions for human intervention in critical decision-making scenarios.
6. Ethical Use
AI should be used to benefit society, avoiding applications that could harm individuals or communities.
Key Components of AI Governance
1. Policy Frameworks
Organizations should establish policies that outline AI development, deployment, and monitoring practices.
2. Risk Management
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with AI, such as bias, misuse, and security vulnerabilities.
3. Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous evaluation of AI systems to ensure they perform as intended and remain aligned with ethical and legal standards.
4. Stakeholder Engagement
Involving diverse stakeholders, including regulators, customers, and internal teams, to ensure AI systems meet societal expectations.
5. Training and Education
Providing employees with the knowledge and skills needed to understand and implement AI governance principles.
Implementing AI Governance in Organizations
1. Establish an AI Governance Committee
Form a cross-functional team to oversee AI governance efforts, including representatives from legal, IT, HR, and other key departments.
2. Develop Ethical Guidelines
Create a code of ethics for AI that reflects the organization’s values and aligns with industry best practices.
3. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Identify potential risks in AI systems and create strategies to mitigate them.
4. Adopt Explainable AI (XAI)
Implement algorithms and models that provide clear, interpretable outputs, enhancing transparency.
5. Leverage Compliance Tools
Utilize tools and platforms to automate compliance monitoring and reporting for AI systems.
6. Integrate Governance into the AI Lifecycle
Incorporate governance practices at every stage, from data collection and model development to deployment and post-deployment monitoring.
Challenges in AI Governance
1. Rapid Technological Advancements
AI technology evolves faster than regulatory frameworks, making it challenging to keep governance policies up to date.
2. Complexity of AI Models
Deep learning models and other advanced algorithms are often opaque, complicating transparency and accountability efforts.
3. Global Disparities in Regulation
Different countries have varying AI governance standards, creating challenges for multinational organizations.
4. Data Privacy Issues
Balancing data access for AI training with privacy concerns remains a significant hurdle.
5. Lack of Standardization
The absence of universal AI governance standards leads to inconsistent practices across industries and regions.
Regulatory Landscape for AI Governance
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Europe’s GDPR emphasizes data privacy and accountability, influencing AI governance practices globally.
2. EU AI Act
A proposed framework for classifying AI systems based on risk levels, mandating stricter regulations for high-risk applications.
3. US AI Initiatives
Various federal and state-level efforts focus on developing AI governance guidelines, including the AI Bill of Rights.
4. Asia-Pacific Regulations
Countries like China and Japan are crafting unique approaches to AI governance, balancing innovation with ethical considerations.
5. Industry Standards
Organizations like ISO and IEEE are working on creating global standards for AI governance and ethics.
Emerging Trends in AI Governance
1. AI Ethics Boards
Establishing dedicated ethics boards within organizations to oversee AI development and deployment.
2. AI Accountability Laws
New regulations are emerging to assign legal responsibility for AI decisions, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance.
3. Decentralized AI Governance
Using blockchain and decentralized technologies to create transparent and tamper-proof AI governance frameworks.
4. AI for Governance
Leveraging AI tools to monitor compliance, assess risks, and ensure adherence to governance principles.
5. Collaborative Governance Models
Public-private partnerships and multi-stakeholder initiatives are shaping global AI governance policies.
Case Study: AI Governance in Action
Scenario: Financial Services
A multinational bank adopted an AI governance framework to manage its algorithmic trading platform.
- Challenges: Managing bias, ensuring compliance with financial regulations, and maintaining transparency.
- Solutions:
- Developed an AI ethics charter.
- Implemented regular audits of trading algorithms.
- Leveraged explainable AI techniques for decision traceability.
- Outcomes:
- Reduced regulatory violations.
- Increased customer trust through enhanced transparency.
Conclusion
AI governance is a crucial element in ensuring the responsible and ethical use of AI technologies. By establishing clear policies, managing risks, and fostering transparency, organizations can harness the potential of AI while safeguarding against its challenges. As regulations evolve and new technologies emerge, staying proactive in AI governance will be essential for sustainable growth and innovation.