Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that has been growing in popularity over the last few years. However, many people still do not understand what RPA is and how it works. In this article, we will explain RPA in plain English, so that anyone can understand it.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic process automation services are a technology that uses software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks. RPA bots are programmed to mimic human actions, such as opening emails, copying and pasting data, and filling out forms. This allows businesses to automate tasks that were previously done manually, which can lead to significant efficiency gains and cost savings.
How does RPA work?
RPA works by using software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks. The bots are programmed to follow a set of instructions that tell them what to do. For example, a bot might be programmed to open an email, read its contents, and then enter the information into a database. The bot can do this much faster and more accurately than a human could.
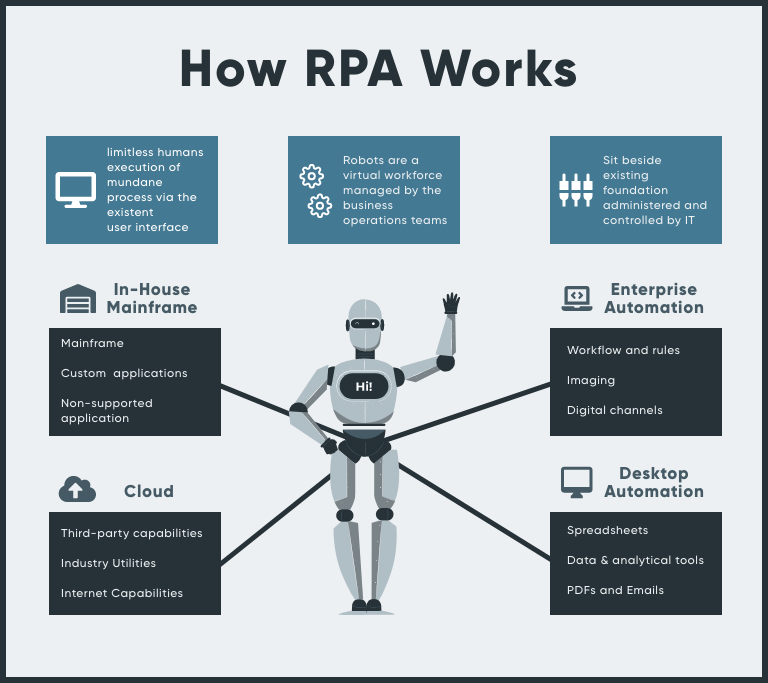
To program an RPA bot, developers use a visual drag-and-drop interface to create a workflow. The workflow consists of a series of steps that the bot will follow. Each step can be customized to meet the specific needs of the business. Once the workflow is complete, the bot can be deployed to automate the task.
What are the benefits of RPA?
RPA offers a wide range of benefits to businesses that implement it. Here are some of the main benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: RPA can automate tasks faster and more accurately than humans, which can lead to significant efficiency gains.
- Cost Savings: RPA can help businesses reduce costs by eliminating the need for manual labor.
- Improved Accuracy: RPA can reduce errors and improve accuracy by eliminating manual data entry and other tasks that are prone to errors.
- Better Customer Service: RPA can help businesses improve customer service by providing personalized and responsive interactions.
- Scalability: RPA can be easily scaled to meet changing business needs.
- Faster Processing Times: RPA can automate tasks faster than humans, which can lead to faster processing times.

- Improved Analytics: RPA can help businesses improve their analytics by providing real-time data and insights.
- Increased Productivity: RPA can help businesses increase productivity by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
- Improved Compliance: RPA can help businesses improve compliance by ensuring that tasks are completed in a consistent and standardized manner.
- Increased Competitive Advantage: RPA can provide businesses with a competitive advantage by improving their efficiency, productivity, and customer service.
What are some examples of RPA?
RPA can be used in a wide range of industries and applications. Here are some examples of how RPA is being used today:
- Finance and Accounting: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as accounts payable and accounts receivable.
- Human Resources: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as employee onboarding and offboarding.
- Healthcare: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as patient registration and claims processing.
- Customer Service: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as responding to customer inquiries and requests.
- Manufacturing: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as inventory management and order processing.
Is RPA the same as Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Process and AI are related technologies, but they are not the same thing. Robotic Process Automation is focused on automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, while AI is focused on developing systems that can learn and make decisions on their own. Robotics uses rules-based logic to automate tasks, while AI uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data and make

