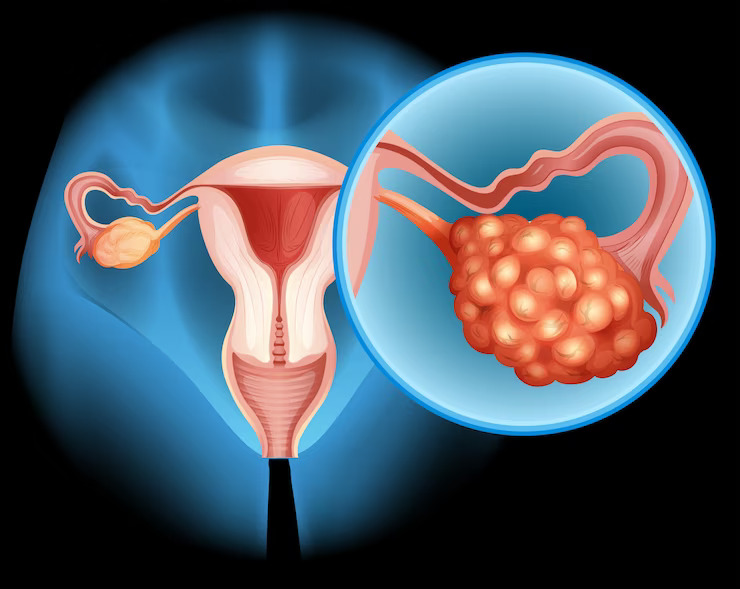
Ovarian cysts are common formations within or on the surface of ovaries. The most common types aren’t harmful, lack symptoms, and eventually subside independently. However, a few types of ovarian cysts necessitate surgical removal of the cyst.
The ovarian cyst size for surgery varies depending on the type of ovarian cyst you have. In this article, you’ll learn about the types of ovarian cysts and the surgical treatment available for them.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are of various types, each resembling similar symptoms. In most cases, the ovarian cysts are functional. It means they start developing within or outside the ovary due to hormonal fluctuations associated with your menstrual cycle.
Functional cysts are ovulation-related growths that have no connection to any disease activity; they frequently go away independently. Some more cyst types include:
1. Follicular Cysts
Your ovary consists of a follicle. It releases an egg every time you ovulate. A cyst may develop on your ovary if you don’t produce an egg over the month because the follicle may become swollen with fluid.
2. Corpus Luteum Cysts
The lining of the corpus luteum develops when your ovary discharges an egg. This corpus luteum is a collection of cells that releases hormones at the time of ovulation. Your ovary develops a cyst whenever it becomes clogged with fluid.
3. Endometriomas
Endometrial tissue can develop into cysts called endometriomas. The lining of your uterus that sheds during your monthly cycle is called endometrial tissue. Endometriosis patients frequently develop these cysts.
4. Dermoid Cysts
Dermoid cysts, also popularly called teratomas, are a clump or collection of various distinct tissues in your body. These cysts, which develop on your ovary, include skin, teeth, and hair components. They grow from the ovarian reproductive cells.
Other Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts do not always develop in conjunction with your menstrual cycle. The other types are:
- Cystadenomas. These cysts develop on your ovary’s surface. They may be filled with thin, viscous fluid or thicker, mucus-like fluid.
- Ovarian Cancer Cysts: These are clumps of cancerous cells that develop in your ovary over time.
Surgical Treatment Options For Ovarian Cysts
Surgical removal is typically required for ovarian cysts that are big, persistent, or aggravating symptoms. Doctors recommend surgery when they worry the cysts may turn malignant and develop cancerous cells.
Depending on the ovarian cyst size for surgery, your surgeon may recommend one of these surgery options:
- Laparoscopy
- Laparotomy
Let’s learn more about these ovarian cyst surgical treatment procedures.
Laparoscopy
Surgeons use laparoscopy—a minimally invasive surgical procedure—to remove the cysts in your ovaries. During a laparoscopic cystectomy, the surgical team will implant the necessary instruments to remove the cyst through one or more small abdominal incisions.
Recovery from this surgical procedure is considerably faster. Most patients can return to their day-to-day life within a week after laparoscopy.
Typically, a session of laparoscopy takes about an hour, based on the complexity of the procedure and the patient’s condition. The surgeon keeps the patient in their post-op or recovery room for a couple of hours of observation.
Laparotomy
If cancer is suspected, the surgeon does a laparotomy that entails making a bigger cut into the abdomen.
A deeper cut is done into the abdomen for the surgery. Due to the magnitude of the surgery, a patient can anticipate extended recovery durations.
What Happens After an Ovarian Cyst Surgery?
Everyone’s recovery following surgery differs based on their health status. Most people experience stomach pain after the surgical removal of their ovarian cyst, but this should subside in a few days.
Upon successful laparotomy, you’ll have to rest for at least 12 weeks to get back on your feet and daily life activities. After surgery, the doctor will send your cyst for further examination. Once the results come, the doctor will decide whether you need additional cyst treatment.
During the recovery phase, if you experience the symptoms listed below, you may require the doctor’s attention and perhaps some additional treatment. These symptoms are:
- Swelling in the abdomen or severe pain
- Heavy bleeding
- Smelly or dark vaginal discharge
- High temperature
Conclusion
If your physician discovers an ovarian cyst during a pelvic exam or ultrasound, don’t be alarmed; they are frequent and typically harmless.
For the best treatment, consult the gynaecologists at reputed hospitals. They have extensive experience dealing with surgeries and patients with ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer.
Follow their advice for the next steps if they uncover a cyst that needs further diagnosis.